
Space
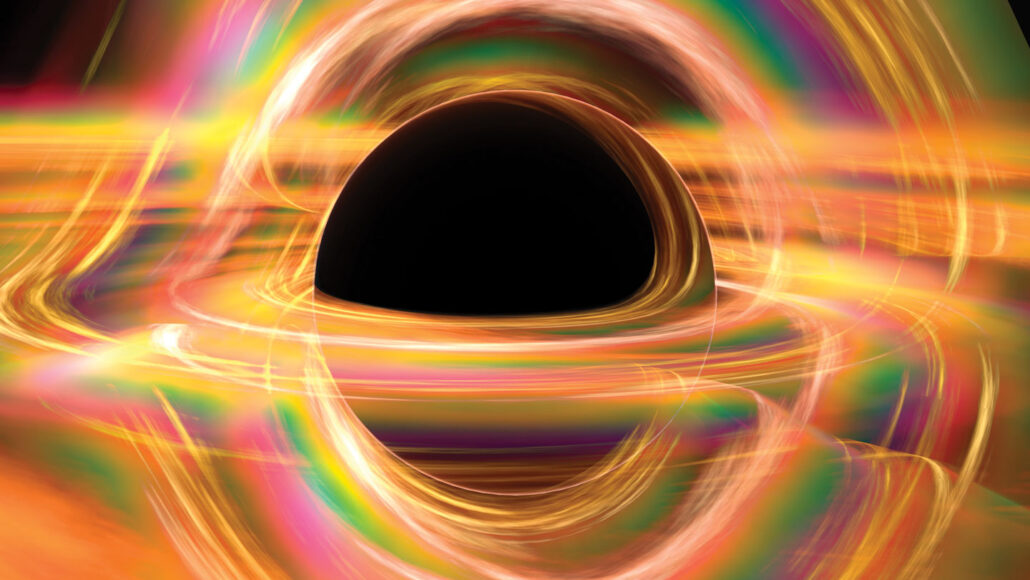
Weird black holes may reveal secrets of the early universe
Emerging evidence points to the existence of rogue black holes and other cosmic oddities — such as big black holes in tiny galaxies.
Come explore with us!

Emerging evidence points to the existence of rogue black holes and other cosmic oddities — such as big black holes in tiny galaxies.

Observations of dead stars hint that ripples in spacetime — ripples light-years long — roll through our universe.
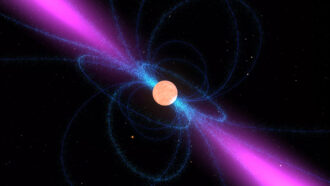
These rapidly spinning dead stars send beams of radio waves into space like cosmic lighthouses.

Data from NASA’s Juno spacecraft hint that Jupiter’s lightning extends in jagged steps as it does on Earth.
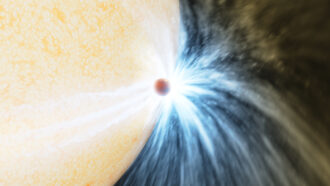
A burst of light and a cloud of dust are signs that a distant star swallowed a giant planet.

Dark voids riddle the galaxies, revealing new details about how stars alter their environments.

The unusual, fruit-inspired structure of this material provides quick filtration that could satisfy people's daily water needs.

Cosmic swirls of gas, dust and plasma, accretion disks reveal the shadowy silhouettes of black holes and more.

Like Luke Skywalker’s home, planets orbiting two stars may be plentiful. A new computer model suggests that many of those worlds could sustain life.
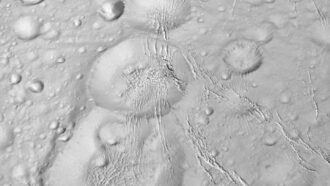
Pits on the frosty moon reveal the snow’s surprising depth, up to 700 meters (2,300 feet) in some places.